Table of Contents
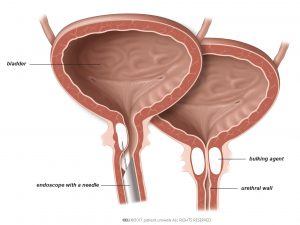
Injection of bulking agents may offer short-term relief but does not cure stress urinary incontinence. Bulking agents can consist of synthetic materials or bovine collagen. The substance is injected into the urethral wall to aid urethral closure. The effect wears off over time. There is a risk that the injection will lead to temporary problems emptying the bladder.
When should I consider a bulking agent injection?
Injection with bulking agents is not recommended if you want a permanent cure for stress urinary incontinence. It can be used if you cannot have other treatments or prefer to postpone surgery.
How are bulking agents injected?
For this procedure, local anaesthesia may be used. However, spinal or general anaesthesia can also be an option. This can vary between different countries and departments.
Steps:
How do I prepare for the procedure?
Before the procedure, the doctor will ask for a urine sample to make sure you do not have a urinary tract infection. If you have an infection, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
After the procedure
How long will it take me to get back to my daily activities?
If you are unable to urinate without any problems and there is not much residual urine in the bladder, you will be discharged from the clinic.
For 3-4 weeks your doctor may recommend to:
- Consume enough liquid, especially water, to provide at least 2 litres of urine output
- Not lift anything heavier than 5 kilograms
- Not do any heavy exercise
- Take showers instead of baths
- Avoid thermal baths, or going to the sauna
- Prevent constipation by adapting your diet
- Avoid sexual activity
- Avoid activities which can traumatise the operation such as cycling and horseback riding.
Call your doctor or go back to the hospital right away if you:
- Have a fever
- Are unable to urinate
- Have heavy blood loss or pain
- Notice the wounds start to bleed or leak fluid, or hurts
- Notice swelling, pain, or redness in the scrotum