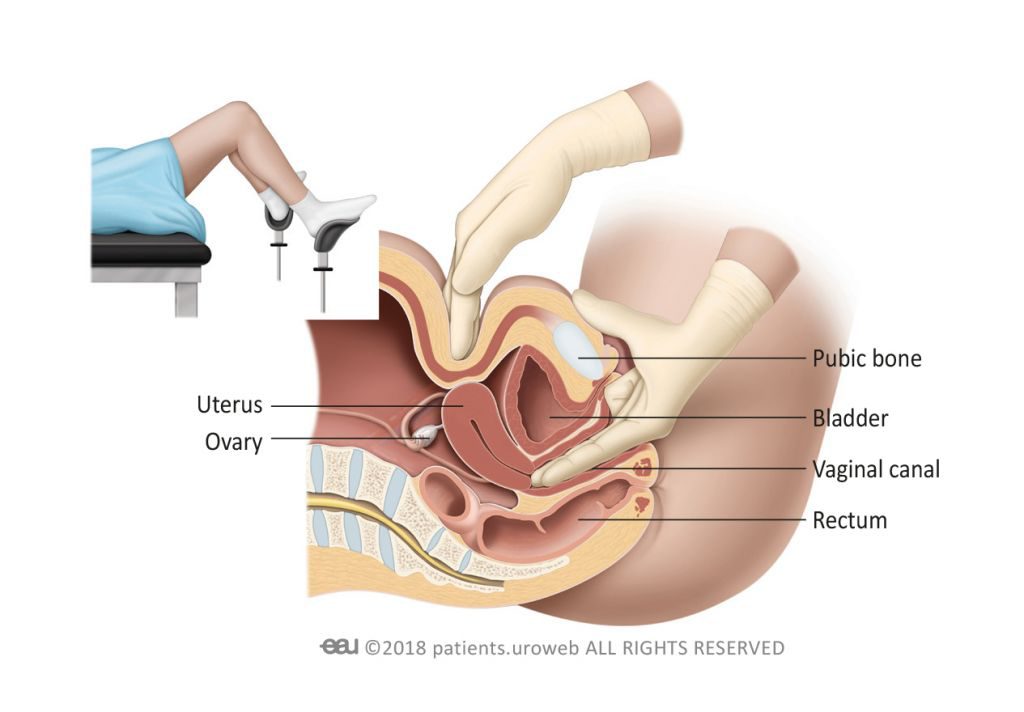
A bimanual exam is performed with two hands. The doctor uses this two-handed exam to check the size and location of a woman’s pelvic organs (such as the uterus and ovaries). This exam is routine in women’s health care (gynaecology). In urology, it is used to diagnose problems related to urination, including cancer.
The doctor wears gloves on both hands. Using lubrication, the doctor inserts two fingers into the woman’s vagina and then presses her abdomen with the other hand (Figure 1). The whole abdomen will be pressed from inside and outside to feel the internal organs. If pressing the organs causes pain, tell the doctor.
In men, the doctor performs a bimanual exam when there is suspicion of advanced prostate- or bladder cancer. In this case, the doctor inserts one finger in the rectum and places the other hand on the abdomen.