Electrical stimulation involves having a device called an electrode placed near a nerve so it can send an electric current to artificially activate the muscle. As with all treatments, electrical stimulation may not be suitable for everyone, but your doctor will be able to discuss this with you.
Electrical stimulation can feel a little uncomfortable at first, but it is not painful. The treatment usually starts with a low level of intensity which may be increased, but only up to a certain point where you still feel comfortable.
To help relieve urinary incontinence, your doctor may offer you different types of electrical stimulation including sacral nerve stimulation, tibial nerve stimulation, or pelvic floor stimulation.
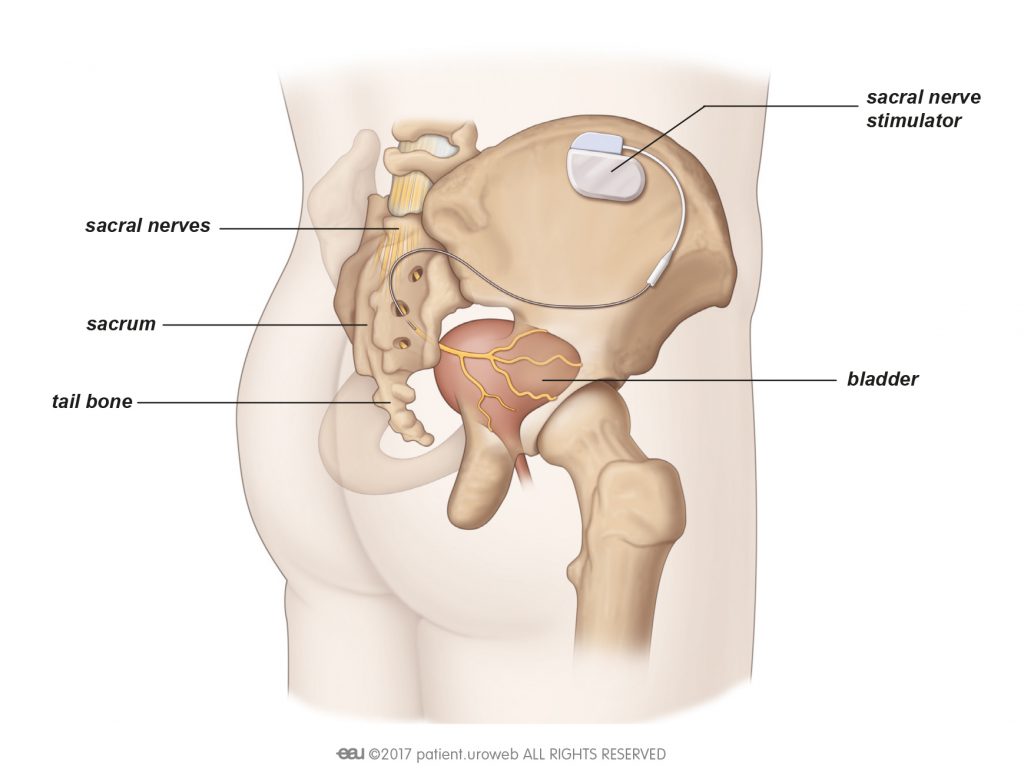
Sacral nerve stimulation
You have a network of nerves (called a plexus) in the lower half of your body, near the base of your spine. This particular network is called the sacral plexus. Your sacral nerves are found in the thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis.
If your doctor recommends trying sacral nerve stimulation, you will need to have a thin wire (called an electrode) and a control unit inserted under your skin. The procedure is done under a local or general anaesthetic.
The control unit is about the size of a mobile phone and is used to change and control the frequency of electrical signals delivered to the electrode, which stimulates the sacral nerves.
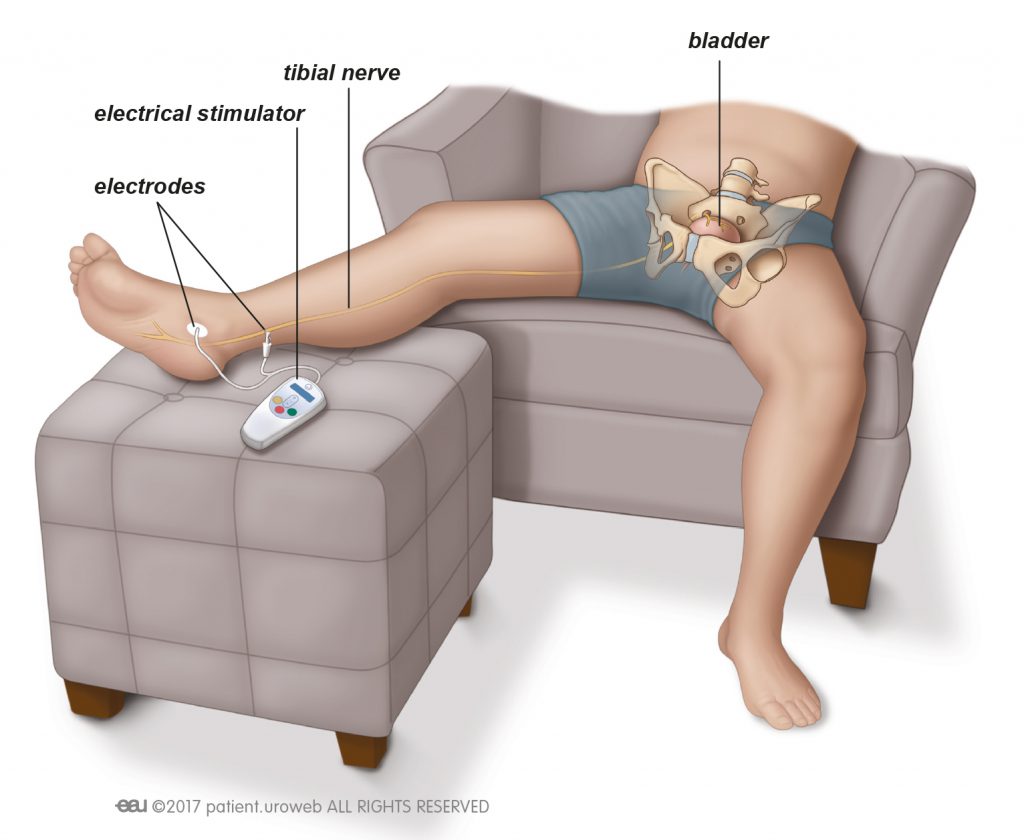
Tibial nerve stimulation
Your sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in your body. It extends from the lower end of your spine, down the back of your thigh, and divides into two branches above the knee. Your tibial nerves are one of these two branches of nerves. Your tibial nerves extend through your leg and foot muscles.
Tibial nerve stimulation involves having a tiny needle inserted into your foot which is used to send electrical pulses to the nerves around your pelvis, which can be helpful if the brain is struggling to activate the muscles necessary for holding urine in the bladder.
Pelvic floor stimulation
Your pelvic floor muscles are a sheet of muscle at the bottom (floor) of the pelvis. The muscles help you to control when you release urine from the bladder. Pelvic floor stimulation can help both women and men contract and strengthen their pelvic floor muscles to address the cause of their urinary incontinence symptoms. Pelvic floor stimulation involves passing a small electrical current through your pelvic floor muscles. The probe is placed in the vagina for women or in the anus for men.