Table of Contents
What is circumcision?
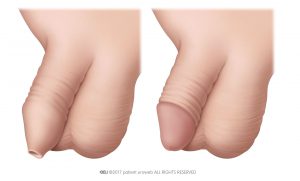
Circumcision is a surgical procedure to remove the foreskin of the penis (Fig. 1). It is used to treat phimosis, a condition in which the foreskin cannot be pulled back over the head of the penis (glans). Phimosis affects only boys and is normal in infants and toddlers. The foreskin typically separates between ages 2 and 6. In most cases, it will detach naturally on its own.
Circumcision is necessary to treat phimosis that results from scarring from previous injury. It can also treat phimosis that causes frequent infections of the foreskin or the urinary tract. Circumcision may be needed if the foreskin causes problems urinating. If phimosis does not get better with the use of steroid creme, circumcision may be needed.
Circumcision is not an option for some patients who have:
- Active problems with heart or lung function or a bleeding disorder
- Foreskin or glans that is actively infected
- Birth defects of the penis
- A penis that urinates through an opening on the underside rather than at the tip (hypospadias)
- A penis that is not visible or is inside the skin (buried penis; foreskin may be needed for a reconstructive procedure)
How is circumcision performed?
The procedure can be performed under local or general anaesthesia.
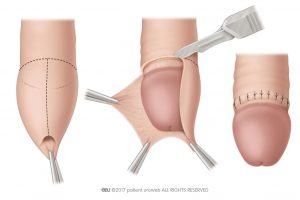
To remove the foreskin, the surgeon holds it with a grasper and cuts the skin away from the penis (Fig. 2). The skin below the glans is stitched to the skin of the shaft to heal. The wound is covered with gauze.
Does circumcision hurt?
In fact, circumcision is not a very painful procedure. Anaesthesia dulls pain during the surgery. Urination does not cause pain after surgery because the urethra (the tube that passes urine from the bladder) is not touched.
Recovery from circumcision
Recovery from circumcision is usually quick:
- Infants, 12-24 hours
- Young children, 1-2 days
- Older children and adults, 3-4 days
Very few patients have problems or side effects after circumcision. Light bleeding or discharge 2-3 days after surgery will stop on its own. Bruising or swelling of the penis skin can last for a few weeks. Treat with cold packs and pain relievers (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, NSAIDs).
Sometimes not enough skin is removed, and another operation is needed. More serious problems like damage or major bleeding are very rare.
Contact your doctor after surgery if the patient:
- Has pus coming out of the wound
- Has a red, painful, or swollen penis
- Has bleeding that will not stop
- Urinates very little or not at all
- Has a fever